
Working directory - this is the directory in which jobs are prepared and results/output files are stored. Simulation options - these include the choice of simulation controller to use (only local batch controller is provided in this version), the number of processors (cores) to deploy, the working directory of the project, and options to keep/remove temporary files after the simulation.

Several methods are provided for creating a batch that is a subset of all jobs defined by the project. jEPlus creates batch jobs according to the batch configuration defined by the user and systematically names each job before carrying out simulations with EnergyPlus. It is also used for naming output directories of jobs.Ī batch of jobs (a batch) – a collection of jobs of a parametric study. Job ID - Each EnergyPlus job is named systematically, following a simple rule: G_-T_-W_-_-_-…A job's id is a unique identification of the job within a project. 'A job' can refer to a model to be simulated, or the process of a simulation. These files typically include either an IDF, an IMF, or a set of IMF/IDF files, a weather file, and a RVI or MVI file. The weather file to be used in simulation can be a parameter, too.Īn EnergyPlus job (a job) – a set of input files defining a model for EnergyPlus to simulate. an HVAC system), and even the whole model (the model template can be regarded as a parameter). the construction of an external wall), a sub-system (e.g. a temperature set point), a component (e.g. A parameter can be a single design variable (e.g. Parameter – an element or aspect of the model that can have more than one options. Search strings are used by jEPlus to identify locations in the model to insert values for parameters. Search string – a specially formulated text string that are not normally occurring in EnergyPlus files. A template should be based on a working EnergyPlus building model. Model template – an IDF (.idf) file or a set of IMF (.imf) files that contains search strings (see next). These information include: a list of model templates, a list of weather files, one RVI or MVI file, the parameters tree, and simulation settings such as the working directory, number of processors to deploy, and options to keep or remove temporary files and EnergyPlus outputs. JEPlus Project - a jEPlus project contains all nessesary information that defines the parametric study. Register onlineĢ x an hour and a half: From 6:30 pm on December 04-05, 2017.Some key concepts of jEPlus are explained here: Prerequisite Knowledge of Audience: Advanced heat transfer, advanced fluid mechanics & numerical methods. DurationĪcademic researchers & practitioners in the energy simulation community (industry, engineering offices, consultancy offices.
#Input file trnsys software#
Models are constructed in such a way that users can modify existing components or write their own, extending the capabilities of the environment.Īfter 42 years of commercial availability, TRNSYS continues to be a flexible, component-based software package that accommodates the ever-changing needs of both researchers and practitioners in the energy simulation community. The standard library includes approximately 150 models ranging from pumps to multi-zone buildings, wind turbines to electrolyzers, weather data processors to economics routines, and basic HVAC equipment to cutting edge emerging technologies. The second part of TRNSYS is an extensive library of components, each of which models the performance of one part of the system. The kernel also provides utilities that (among other things) determine thermophysical properties, invert matrices, perform linear regressions, and interpolate external data files. The first is an engine (called the kernel) that reads and processes the input file, iteratively solves the system, determines convergence, and plots system variables. While the vast majority of simulations are focused on assessing the performance of thermal and electrical energy systems, TRNSYS can equally well be used to model other dynamic systems such as traffic flow, or biological processes. TRNSYS (pronounced ‘tran-sis’) is an extremely flexible graphically based software environment used to simulate the behavior of transient systems. TRNSYS is one of the powerful fully flexible tools for energy and dynamic systems simulation.
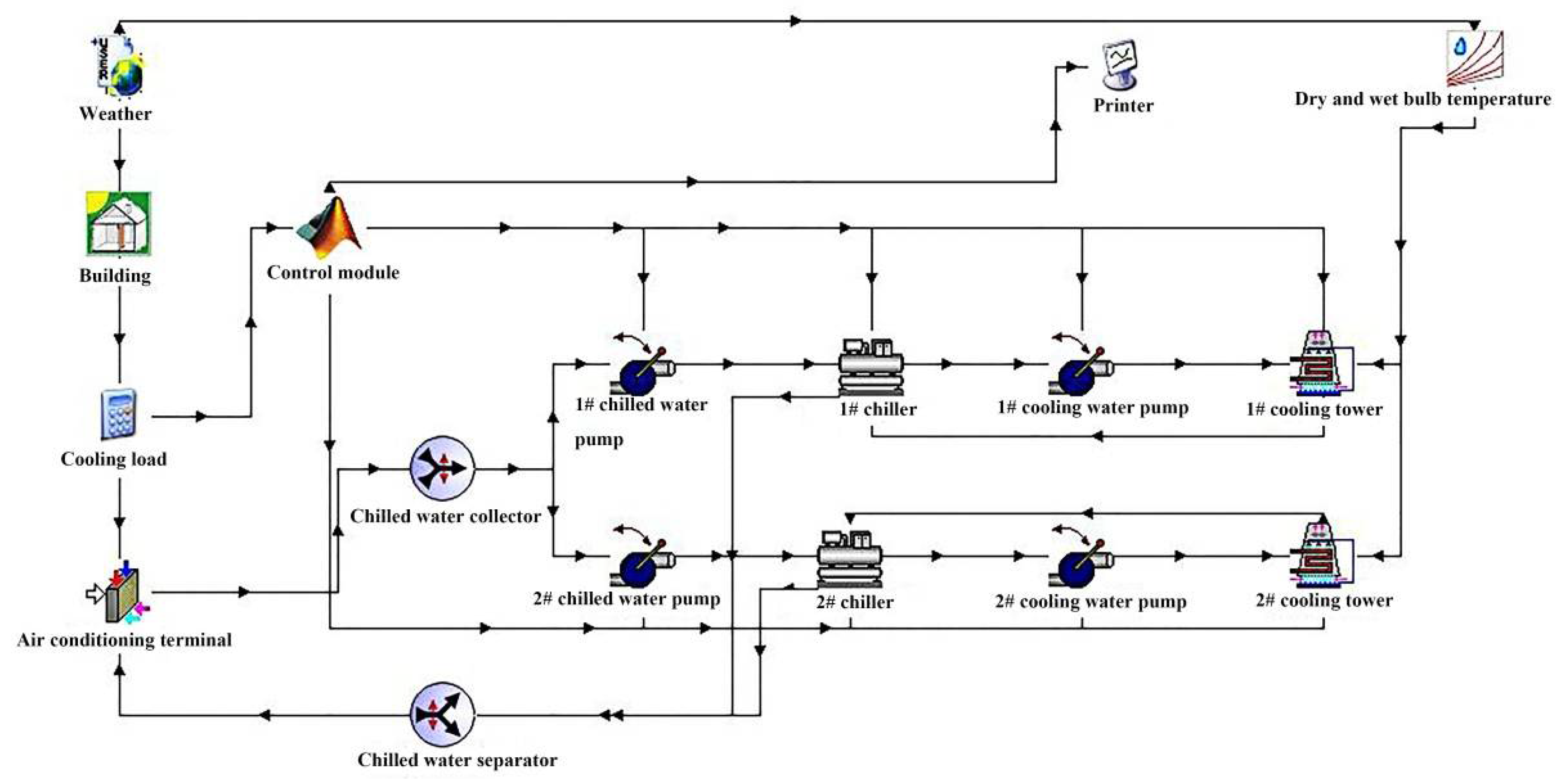
If you do not have a license, a demo version should be installed prior to the tutorial attendance. You should bring your laptop with you if you want to benefit from the hand-on quick exercise.
#Input file trnsys how to#
– Hand-on quick exercise: how to build a mono-zone building simulation.

– Global overview of TRNSYS software capabilities.

Brahim Benhamou, Cadi Ayyad University, Marrakech, Morocco CONTENT – To practice a simple building simulation exercise. – To learn about TRNSYS software capabilities.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
